Investigating the Opportunities and Threats of the Iranian Startup Ecosystem
Keywords:
Startup ecosystem, opportunities, threats, entrepreneurial development, innovation, IranAbstract
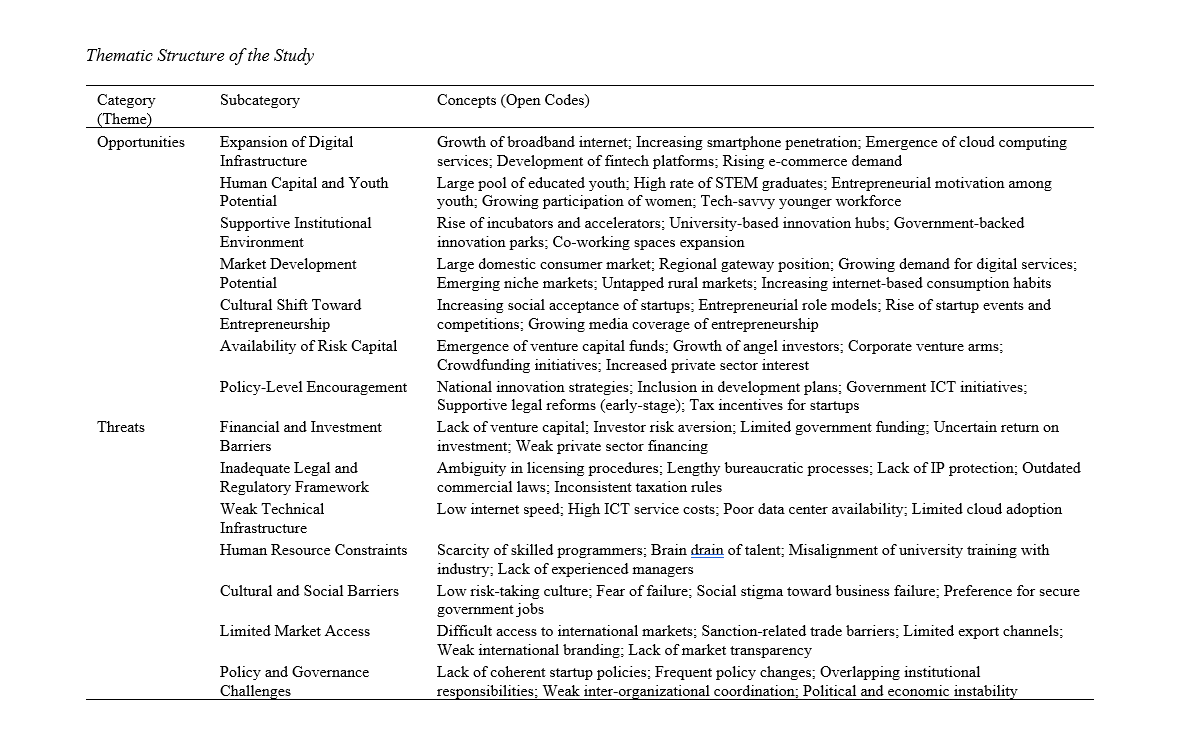
This study aimed to qualitatively explore and analyze the main opportunities and threats shaping the development of the startup ecosystem in Iran, with the goal of informing strategies to strengthen its entrepreneurial infrastructure, policies, and cultural foundations. This research employed a qualitative design using library-based data sources, including academic articles, policy documents, institutional reports, and national statistics related to the Iranian startup ecosystem. A purposive sampling strategy guided the selection of credible and thematically relevant documents, and data collection continued until theoretical saturation was achieved. All textual data were imported into NVivo 14 for systematic analysis through a three-stage coding process—open, axial, and selective coding—based on thematic content analysis. Emerging codes were constantly compared to ensure consistency and reliability in theme development. The analysis revealed two overarching categories—opportunities and threats—comprising multiple subthemes. Opportunities included the expansion of digital infrastructure, the availability of youthful human capital, the rise of institutional support structures, growing domestic market potential, increasing cultural acceptance of entrepreneurship, emerging access to risk capital, and policy-level encouragement. Conversely, key threats involved financial and investment barriers, legal and regulatory uncertainty, weak technical infrastructure, human resource constraints, cultural and social risk aversion, limited access to international markets, and fragmented policy governance. These findings highlight a dual reality in which promising enablers coexist with structural constraints that impede ecosystem maturation. The Iranian startup ecosystem is in a transitional stage, endowed with significant assets yet constrained by systemic weaknesses. Strategic interventions addressing funding gaps, regulatory reform, infrastructure upgrading, talent development, and cultural change are essential to transform Iran’s entrepreneurial potential into a sustainable engine for innovation-driven economic growth.
References
Abbasian, S., Khosravi, M., & Hosseini, A. (2019). Institutional Support and Startup Survival in Iran's Entrepreneurial Ecosystem.
Abreu, M., & Grinevich, V. (2013). The nature of academic entrepreneurship in the UK: Widening the focus on entrepreneurial activities. Research Policy, 42(2), 408-422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2012.10.005
Amini, A. (2022). The effect of transformational leadership on job commitment according to the mediating role of organizational resilience. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS), 3(1), 480-489. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.3.1.38
Chaudhari, S. L., & Sinha, M. (2021). A Study on Emerging Trends in Indian Startup Ecosystem: Big Data, Crowd Funding, Shared Economy. International Journal of Innovation Science. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijis-09-2020-0156
Diaz-Carrion, F. L. (2021). A dynamic analysis of the role of entrepreneurial ecosystems in reducing innovation obstacles for startups. Journal of Business Venturing Insights, 14(3), 145-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbvi.2020.e00192
Feng, N., Fu, C., Wei, F., Peng, Z., Zhang, Q., & Zhang, K. H. (2019). The key role of dynamic capabilities in the evolutionary process for a startup to develop into an innovation ecosystem leader: An in-depth case study. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 54, 81-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2019.11.002
Font-Cot, F., Navarra, P. L., & Serradell-López, E. (2023). Digital Transformation Policies to Develop an Effective Startup Ecosystem: The Case of Barcelona. Transforming Government People Process and Policy, 17(3), 344-355. https://doi.org/10.1108/tg-01-2023-0006
Gol Ara, P., Adib Saber, F., & Nasiri, M. (2024). Conceptualizing the Digital Entrepreneurship Ecosystem in Iran: An Effort to Develop Sports Startups. Journal of Entrepreneurship Research, 3(4), 77-92. https://ijnaa.semnan.ac.ir/article_8579.html
Gupta, R. K. (2022). Does University Entrepreneurial Ecosystem and Entrepreneurship Education Affect the Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention/Startup Intention? In Industry 4.0 and Advanced Manufacturing: Proceedings of I-4AM 2022 (pp. 355-365). Springer.
Haines, T. (2016). Developing a startup and innovation ecosystem in regional Australia. Technology Innovation Management Review, 6(6), 24-32. https://www.timreview.ca/sites/default/files/Issue_PDF/TIMReview_June2016.pdf#page=24
Kahraei, S., & Shivaei, E. (2021). Investigating the Impact of the Development of Knowledge-Based Companies and Innovative Startups in Science and Technology Parks on Regional Economic Growth in Iran. Innovation Ecosystem Quarterly, 1(2). https://innoeco.usb.ac.ir/article_6619.html?lang=en
Mondalizadeh, Z. (2024). Startup opportunities in the sports industry based on developing a conceptual framework for the sports ecosystem in Iran. Interdisciplinary Journal of Management Studies, 17(2), 491-506. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJMS.2023.339962.675079
Moradi, S., Abbasi, J., Radfar, R., & Abdolvand, M. A. (2024). Qualitative Identification of Intervening Factors Affecting Digital Marketing Strategies in Successful Iranian Startups. International Journal of Innovation Management and Organizational Behavior (IJIMOB), 4(2), 46-53. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.ijimob.4.2.6
Peixoto, Â., Gouveia, T, Sousa, P, Faria, R, Almeida, P. R. (2023). Dark personality traits and tolerance towards unethical behaviors on entrepreneurship: A comparison between entrepreneurs and non-entrepreneurs. Journal of White Collar and Corporate Crime, 4(1), 5-13. https://doi.org/10.1177/2631309x211029877
Rocha, C. F., Mamédio, D. F., & Quandt, C. O. (2019). Startups and the innovation ecosystem in Industry 4.0. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 31(12), 1474-1487. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2019.1628938
Sevilla-Bernardo, J., Sanchez-Robles, B., & Herrador-Alcaide, T. C. (2022). Success factors of startups in research literature within the entrepreneurial ecosystem. Administrative Sciences, 12(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12030102
Smachylo, V., Dymchenko, O., Rudachenko, O., Bozhydai, I., & Khailo, Y. (2024). Formation of Strategies for the Development of Startup Ecosystems as a Prerequisite for Sustainable Entrepreneurship In: Semenov, A., Yepifanova, I., Kajanová, J. (eds) Data-Centric Business and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53984-8_1
Thomas, A., Passaro, R., & Quinto, I. (2020). Developing Entrepreneurship in Digital Economy: The Ecosystem Strategy for Startups Growth. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85423
Tripathi, N., Oivo, M., Liukkunen, K., & Markkula, J. (2019). Startup ecosystem effect on minimum viable product development in software startups. Information and Software Technology, 114, 77-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2019.06.008
Tripathi, N., Seppänen, P., Boominathan, G., Oivo, M., & Liukkunen, K. (2019). Insights Into Startup Ecosystems Through Exploration of Multi-Vocal Literature. Information and Software Technology, 105, 56-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2018.08.005
Weingarth, J., Hagenschulte, Julian, Schmidt, Nikolaus, Balser, Markus. (2019). Building a Digitally Enabled Future: An Insurance Industry Case Study on Digitalization. In Digitalization Cases: How Organizations Rethink Their Business for the Digital Age (pp. 249-269). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95273-4_13
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Payam Khodagholi (Author); Soheila Sardar; Seyed Abdollah Amin Mousavi, Nazi Mohamadzadeh Asl (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









