Designing a Conceptual Model for Human Resource Performance Evaluation Indicators in the Banking Industry with Emphasis on the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Keywords:
Performance evaluation, Human resources, Fourth Industrial Revolution, Banking industryAbstract
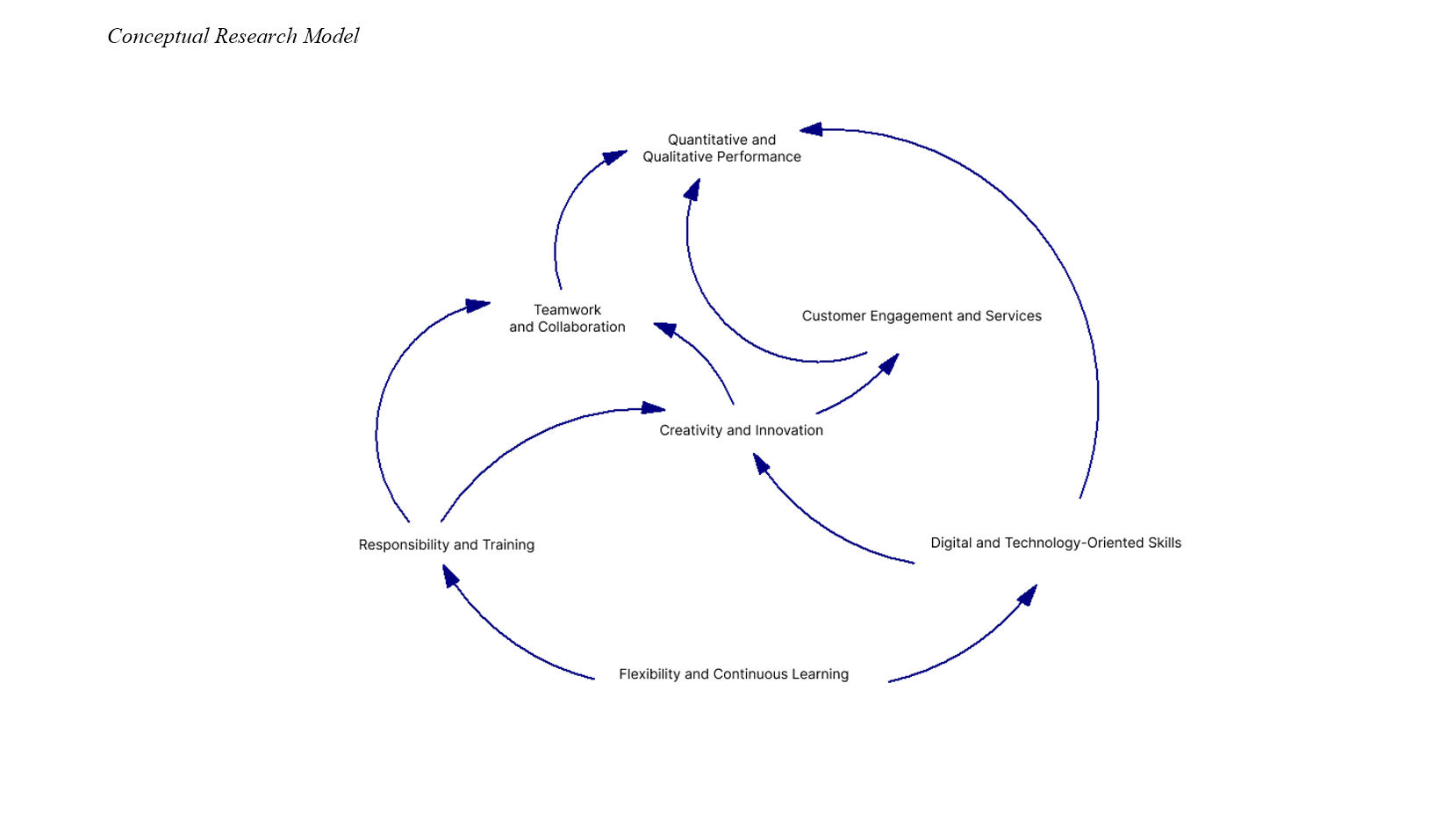
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has not only introduced profound technological transformations but also brought about significant changes in business models and customer demands. In this context, human resources, as the most critical asset of organizations, play a key role in achieving these new objectives. Consequently, evaluating human resource performance has become one of the most crucial areas of organizational focus. This study aimed to design a conceptual model of human resource performance evaluation indicators in the banking industry, with a specific emphasis on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The statistical population of this research was divided into two groups: fifteen subject-matter experts familiar with the research topic, and all senior, middle, and junior managers at various management levels within Bank Melli Iran. A sample of 335 individuals was selected from this population. Data were collected using three separate questionnaires. To analyze the data, fuzzy screening methods, exploratory factor analysis, and Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) were employed. The results of the fuzzy screening indicated that out of a total of 49 human resource performance evaluation indicators, 8 were eliminated, and 41 were confirmed by the experts. Moreover, the findings from the exploratory factor analysis showed that the 41 confirmed indicators could be categorized into seven main components. Finally, the results of the ISM phase revealed that flexibility and continuous learning constitute the foundation of the human resource performance evaluation model with an emphasis on the Fourth Industrial Revolution and are considered the most influential components within the model. In contrast, the component of quantitative and qualitative performance was identified as the most affected component in the structure of the proposed model.
References
Aguinis, H. (2009). An expanded view of performance management Untag Samarinda Universitas]. https://vulms.vu.edu.pk/Courses/HRM713/Downloads/PERFORMANCE%20MANAGEMENT%20Performance%20management%20%20putting%20research%20into%20action.pdf#page=35
Amos, K. J., & Natamba, B. (2015). The impact of training and development on job performance in Ugandan banking sector. Journal on Innovation and Sustainability Risus, 6(2), 65-71. https://doi.org/10.24212/2179-3565.2015v6i2p65-71
Arromba, I. F., Martin, P. S., Cooper Ordonez, R., Anholon, R., Rampasso, I. S., Santa-Eulalia, L. A., & Quelhas, O. L. G. (2021). Industry 4.0 in the product development process: benefits, difficulties and its impact in marketing strategies and operations. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 36(3), 522-534. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-01-2020-0014
Ayers, R. S. (2015). Aligning individual and organizational performance: Goal alignment in federal government agency performance appraisal programs. Public Personnel Management, 44(2), 169-191. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091026015575178
Bayraktar, O., & Ataç, C. (2018). The effects of Industry 4.0 on Human resources management. Globalization, institutions and socio-economic performance. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Aykut-Yaglikara/publication/364660800_Relationship_Between_Economic_Freedom_and_Innovation_Panel_Data_Analysis/links/63567e8812cbac6a3eef93ab/Relationship-Between-Economic-Freedom-and-Innovation-Panel-Data-Analysis.pdf#page=338
Cardy, R., & Leonard, B. (2014). Performance Management: Concepts, Skills and Exercises. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315701790
Challoumis, C., & Eriotis, N. (2024). A historical analysis of the banking system and its impact on Greek economy. Edelweiss Applied Science and Technology, 8(6), 1598-1617. https://doi.org/10.55214/25768484.v8i6.2282
Cirillo, V., Fanti, L., Mina, A., & Ricci, A. (2023). The adoption of digital technologies: Investment, skills, work organisation. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 66, 89-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2023.04.011
Ghandour, A. (2021). Opportunities and challenges of artificial intelligence in banking: Systematic literature review. Tem Journal, 10(4), 1581-1587. https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM104-12
Hecklau, F., Galeitzke, M., Flachs, S., & Kohl, H. (2016). Holistic approach for human resource management in Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP, 54, 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.05.102
Hernandez-de-Menendez, M., Morales-Menendez, R., Escobar, C. A., & McGovern, M. (2020). Competencies for industry 4.0. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (Ijidem), 14, 1511-1524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-020-00716-2
Kamble, S. S., Gunasekaran, A., Ghadge, A., & Raut, R. (2020). A performance measurement system for industry 4.0 enabled smart manufacturing system in SMMEs-A review and empirical investigation. International Journal of Production Economics, 229, 107853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107853
Lertpiromsuk, S., Ueasangkomsate, P., & Sudharatna, Y. (2021). Skills and human resource management for Industry 4.0 of small and medium enterprises. Proceedings of Sixth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology: ICICT 2021, London.
Miah, M. T., Erdei-Gally, S., Dancs, A., & Fekete-Farkas, M. (2024). A Systematic Review of Industry 4.0 Technology on Workforce Employability and Skills: Driving Success Factors and Challenges in South Asia. Economies, 12(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies12020035
Moallem, A. (2021). Smart and Intelligent Systems: The Human Elements in Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Cybersecurity. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003215349
Murugesan, U., Subramanian, P., Srivastava, S., & Dwivedi, A. (2023). A study of artificial intelligence impacts on human resource digitalization in Industry 4.0. Decision Analytics Journal, 7, 100249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2023.100249
Nasiri, M., Ukko, J., Saunila, M., Rantala, T., & Rantanen, H. (2020). Digital-related capabilities and financial performance: the mediating effect of performance measurement systems. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 32(12), 1393-1406. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2020.1772966
Ochieng, E. M. (2023). A Study of the History Functions Roles and Challenges of Human Resources Management. Journal of Enterprise and Business Intelligence, 3(1), 054-064. https://doi.org/10.53759/5181/JEBI202303006
Pahuja, S., Mahlawat, S., Kumar, V., Sah, R. K., Paliwal, M., Singh, S., & Kumar, M. (2024). Gaining competitive advantage status through human resource practices: A study of Indian banks. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 9, 100804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2024.100804
Paramesha, M., Rane, N. L., & Rane, J. (2024). Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and blockchain in financial and banking services: A comprehensive review. Partners Universal Multidisciplinary Research Journal, 1(2), 51-67. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4855893
Parida, V., Sjödin, D., & Reim, W. (2019). Reviewing literature on digitalization, business model innovation, and sustainable industry: Past achievements and future promises. Sustainability, 11(2), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020391
Prashar, A., Tortorella, G. L., & Sreedharan, V. R. (2023). Role of organizational learning on industry 4.0 awareness and adoption for business performance improvement. Ieee Transactions on Engineering Management, 71, 4904-4917. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2023.3235660
Reznik, L. (2021). Intelligent Security Systems: How Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Data Science Work for and Against Computer Security. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119771579
Rüßmann, M., Lorenz, M., Gerbert, P., Waldner, M., Justus, J., Engel, P., & Harnisch, M. (2015). Industry 4.0: The future of productivity and growth in manufacturing industries. 9(1), 54-89. https://inovasyon.org/images/Haberler/bcgperspectives_Industry40_2015.pdf
Salampasis, D. G., Mention, A. L., & Torkkeli, M. (2015). Human resources management and open innovation adoption in the banking sector: a conceptual model. International Journal of Business Excellence, 8(4), 433-457. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBEX.2015.070314
Srinivasan, R., Kumar, M., & Narayanan, S. (2020). Human Resource Management in an Industry 4.0 Era. In The Oxford handbook of supply chain management. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780190066727.013.39
Sujatha, R., Prakash, G., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2022). Cyber Security Applications for Industry 4.0. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003203087
Tahiri, A., Kovaçi, I., & Krasniqi, A. (2020). Human resource management, performance management and employee performance appraisal by SME managers in Kosovo. International Journal of Economics and Business Administration, 8(4), 288-298. https://doi.org/10.35808/ijeba/588
Tubré, T., Arthur, W., & Bennett, W. (2014). General models of job performance: Theory and practice. In Performance Measurement (pp. 175-203). Psychology Press. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781315820996-9/
Vrchota, J., Mařiková, M., Řehoř, P., Rolínek, L., & Toušek, R. (2019). Human resources readiness for industry 4.0. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6010003
Vrchota, J., Volek, T., & Novotná, M. (2019). Factors introducing Industry 4.0 to SMES. Social Sciences, 8(5), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8050130
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Zahra Naderi zarneh, Houshang Taghizadeh, Ghaffar Tari (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









